INTRODUCTION TO THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
What is Banking System
Banking system refers to the structural network of institutions that offer financial services to a country. The member of banking system and the function they typically perform includes:
- Commercial banks that take deposits and make loans
- Investment banks which specialize in capital market issues and trading
- National central banks that issues currency and set monetary policy
The Financial System
Below is how the bank acts as the intermediary between the surplus units (those with the extra money) and the deficit unit (those in need of money)
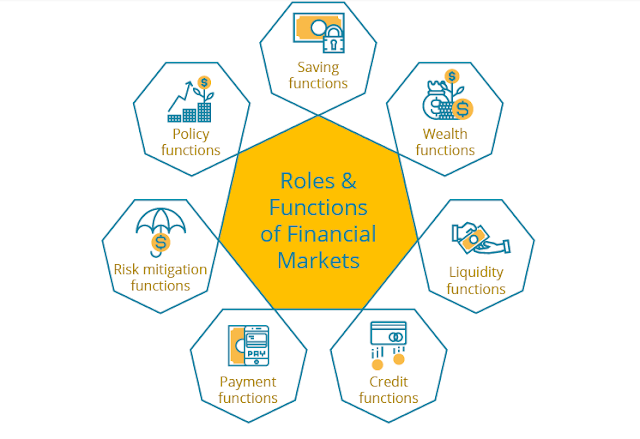
Roles and Functions
What are the role and functions of banks as financial institutions?
Activity: Visiting a Bank
The last time you visited a bank, the 4 W:
- Where were you?
- What was it for?
- When you visited the bank?
- What did you do there?
Activity: The last time I visited the bank to renew my ATM card as my previous card was left inside the ATM machine.
The Role and Functions of Financial Markets
Activity: What did I do?
Activity: Payment Functions: I pay for electricity bill, purchase online goods, recharge voucher, zakat and infaq
The Global Financial Institutions:
Example of Legal and Regulatory Framework ( A Global Perspective)
There is no uniformity of law in governing Islamic Banks around the world. In some countries, special law are enacted by government as a measure to promote and move the Islamic banking industry in the country.
In some other countries, Islamic bank may not be governed by special laws, thus forcing Islamic bank institutions to abide by ordinary laws which governs other financial institutions.
While in some other countries, the dual banking system is practiced where the Islamic and the conventional banking system run in parallel which allows both to compete on a leveled playing field.
Example:
Indonesia ---Indonesia first explored the Islamic banking system in August 1990, when the idea of Islamic bank was explored by the Indonesian Council of Ulema (Majelis Ulama Indonesia - MUI). Subsequently the MUI established a working group to develop plan in establishing an interest free - bank. Furthermore, the involvement of the Association of Indonesia Muslim Intellectual (Ikatan Cendikiawan Muslim Indonesia - ICMI), an organization largely controlled by state, was also important for the realization of the project.
In 1992, Banking Act No. 7 was enacted which allowed Islamic bank to operate in Indonesia in paralled with the conventional institutions (Bank Indonesia 2002). Backed by the government, the first Indonesian Islamic Bank, Bank Muamalat Indonesia (BMI), was established in relatively short time. It started operations on 1 May 1992 (Saeed 2008). 7 years late, the second Islamic bank, Bank Syariah Mandiri (BSM) started operation in Indonesia in November 1999 (Vernados 2011).
In 1998, the Act No. 10 of 1998 on the amendment of the Act No. 7 of 1992 came into force. It allowed Conventional banks to offer Islamic financial services through an islamic unit (window), which is a separate department of a conventional bank dedicated to islamic finance.
A year later in 1999, the Bank of Indonesia Law No. 23 (in 2006 amended by law No. 3) provided the central bank with the authority to develop policies, regulations and instruments with comply with principles of Syariah (Vernados 2011). This directly give the authority of Islamic banks placed under Bank Indonesia (The central Bank of Indonesia) rather than the ministry of Religion or MUI.
In July 2008, the law concerning Shariah (Islamic) banking (Act No 21 of 2008) was passed. The main aim of this legislature was to gather all the previous regulations in one act and to eliminate any existing inconsistencies.
From the story above, the policy decision or enactment of law for Islamic Finance depend on how the regulator / government of the particular country is willing to develop the market. Among the reasons are:
It is a new and a niche market despite its presence for the past decade
It take times and is not feasible for countries to come up with a new regulatory framework
ISLAMIC BANKING PRACTICES
What is Islamic Banking?
Islamic banking system is a system of banking based on the statutes of Islamic law and economics.
- Paying or collecting interest, or riba, is prohibited by Islamic law.
- Sharing profit and loss is a banking principle and shareholder capital and deposits are kept separate to ensure fair revenue sharing.
History of Islamic Banking
Islamic Banking and Finance (IBF) is relatively new compared to conventional banking and finance and mostly operates in dual banking system under conventional economic and financial environment. Did you know that:
- The earliest Islamic Financial institutions can be traced to a savings institution based on profit sharing in Mit Ghamr, Egypt in 1963
- Establishment of the first Islamic bank (Dubai Islamic Bank established in the UAE in 1975, as well as the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) in Saudi Arabia.
Establishment of Islamic Banking and Financial Institutions
Islamic Financial System
The basis of Islamic Banking and Finance (IBF) practice arose from the Shariah requirement which also known as Islamic Law or Islamic Jurisprudence.
The Core Components of Islamic Teachings
The Shariah contain three main components:
- Aqidah
- Fiqh
- Akhlaq
Aqidah - Iman (Faith/Believed in God) - Concern on all form of faith and believe by a Muslim in Allah Almighty and His will, from the fundamental faith in His being to the ordinary beliefs in Individual commands (Ahkam)
Shariah - Islam (Islamic Law) Governing all aspect of life - Concern on all forms of practical actions as a manifestation of the faith and belief which known as Islamic Laws
Akhlaq (Moral & Ethic) - Concern on behavior, attitude and work ethics which should be practice by all Muslim in their actions
Islamic Finance is founded on Shariah Principles which express an explicit intention to meet the financial needs of participants with the integrity and in manner that is just, fair, trustworthy and honest, while ensuring a more equitable wealth distribution (Primer to Islamic Finance (MIFC, BNM) 2008, p.50)
Islamic Econnomic
Nation Economic
Economic of Commerce and Industry
Socio - Economic
Nation Economic:
Macro economy
Economic Policy
Development Program
Incentive scheme and creation of competitive advantages
Creation of revenue and wealth
Creation of employment opportunities
Distribution of wealth
Ensure economic stability
Economic of commerce and industry:
Covers all business and trades activities in commerce and industry for domestic and international
The objective of making profit and wealth accumulation
The activities includes investment, finance, banking and capital mobilization
Entrepreneurial development
Socio - Economic:
Promoting economic and welfare activities
Helping poor people and those needed to have good leaving
Activities in this area includes functions of Baitulmal, collection and distribution of zakat fund, fitrah, donation, wakaf (money/asset granted for public utility)
Providing benevolent loan - qardul hasan - an interest free loan
 |
| Islamic Microfinance - A Feasibility Study in the Albanian Market |
Shariah and Wealth
One of the core component of Islamic teaching is Fiqh (Conduct and Ruling). Fiqh is further divided into two components which is rulings on:
- Man to God relationship
- Man to Man relationship
Conduct and Rulings (Fiqh)
Fiqh is an Islamic Law, governing the way of life of human being. It includes man to God Worships (Ibadat) and man to man relationship (Muamalat).
Fiqh Ibadat - The law governing relationship of man to God relationship. This act of worship is addressed to all but only Muslims are confined to its rules. In Fiqh Ibadat, any form of worship is rendered as haram (prohibited) until stated permissible by the authentic sources of Shariah (eq. Quran, Sunnah, Ijma (Consensus)). For Example, in the obligation of Salah (Prayers). Allah has mentioned in the Quran that prayers are obligatory for Muslims. The Sunnah of Prophet (Phub) further explain the details, where Muslims are to perform five (5) obligatory prayers per day. Thus, any obligatory prayer exceeds or is less than this number is prohibited since the ibadat (act of worship) has been specified in the Quran and/or Sunnah.
Fiqh Muamalat - The law governing man to man activities. Shariah law governing man to man relationship covers vaious aspects of laws in daily life activities such as family, political, criminal, economic activities including trade and finances, etc. Fiqh muamalat, practice the term of all permissible unless proven prohibited , which means, anything relation to Muamalat is originally permissible unless there is substantial evidence from the Holy Quran or Al Hadith or Ijma (Consensus opinion of Islamic Scholar) provided ad proven that such act is impermissible. For Example, in the case of Muamalat, we may use the example of Riba. Riba was originally practiced by the traders even before the time of Prophet until the revelation in the Quran in Surah Al-Baqarah verse 2:275....Allah permitted trading and forbidden Riba....
 |
| The Developing Role of Islamic Banking and Finance: From Local to Global Perspectives |
Maqasid Al - Shariah
Maqasid is from Arabic word that means goals or purposes. What are the purpose of Shariah?:
- To protect the religion (Deen)
- To protect the main / brain of human being
- To protect the life / living of human being
- To protect individual decendants of generation
- To protect assets / wealth of Individuals and public
One of objectives of Shariah is to protect assets / wealth of individuals and public (Maal). Islamic financial products thus should contain more benefits (masalih) and less or no harm (madarah).
In gambling (maisir) and liquor (qimar), there are some sins and some profits. But the sins are greater than the profits
(Al - Baqarah: 168)
Maqasid Al - Shariah in Islamic Banking Practices
The chart show how the Maqasid Al - Shariah applicable in Islamic Banking.
As Shariah is the utmost important aspect in any Islamic related activities, Islamic banking practices needs to be inline with the teaching of Shariah which in turn will uphold the objective of Shariah. As Islamic banking is an important component in Islamic financial System, its play a vital role in providing developing economic stability.
The Islamic financial products hence should meet the aboves objectives:
To develop products that meet the needs of the society
To generate profitability of the products that benefecial to all, Islamic financial institutions, customers and investors etc
To ensure the consumer / customer welfare and protection is upheld
To apply prudent market practices to promote financial stability of IFIs which in turn promote global economic stability
 |
| Islamic Economics and Finance: A Glossary |
Principles of Islamic Banking
Basically Islamic banking is based on Shariah principles which is specified in the Islamic law of transaction. Among the key elements in practicing Islamic banking is the avoidance of prohibited elements.
There are the prohibited elements in Islamic banking. To protect assets / wealth of Individual and public, Allah has prohibited the following elements:
- RIBA (Interest/Usury) - is a price paid for loan money
- MAYSIR (Gambling to secure easy money. Anything involves elements of betting upon happening of uncertain future event.
- GHARAR (Uncertainty/Ambiguity) - The uncertain elements in the contract e.q the existence of goods and price are uncertain.
- Syndicates / Collaboration
- Hiding of defects or weaknesses of the goods to be sold / traded
- Big loss to a party, either to seller or buyer, or contractee or contractor which resulted from business transactions.
As stated in Holy Quran:
Those who devour usury will not stand except as stands one who the satan by his touch hath driven to madness. That is because they say: trade is line usury...(Al Baqarah:275)
If ye do it, take notice of war from Allah and His Messenger...(Al Baqarah: 279)
Islamic financial transactions should be conducted in accordance with Shariah principles. Nevertheless, Shariah compliant financial instruments can be offered bu non Islamic financial institutions provided that the product does not contradict with the principles of Shariah. Similarly, Islamic finance can also be offered to both Muslim and Non - Muslim customers.
Guiding Practices
Islamic Banking (IB) practice supports the principles of no riba, no maysir, no gharar through the following practices:
- Profit - Risk with responsibilty - Legal Maxim (Qawaid Fiqhiyyah) - Al Kharaj bi al Dhamarl and Al Ghunm il Gurm, the criterion of legality of any return in Capital, meaning that one has to bear loss if he wants to earn any profit over his investment
- Islamic Banking financing deals in goods and documents and not money. Money is only the medium of exchange, and a store of value
- Avoiding gambling and game of chance
- Transparency and documentations
Why not the current banking practices?
The main shariah non - compliance elements which exist in todays conventional banking practices is the practices of charging additional charges on loans which translate into price of loan. This additional price is as mentioned above is the practice of Riba (usury).
Classification of Riba - Usury
Classification of Riba - Usury
Buy & Sell:
- Riba Al - Fahdlu (Riba Al Hadees): actually means that excess which is taken in exchange of specific homogenous comodities and encountered in their hand to hand purchace and sale as explained in famous hadith: The Prophet said, sale gold in exchange of equivalent gold, sell silver in exchange of equivalent silver, sell dates in exchange of equivalent dates, sell wheat in exchange of equivalent wheat, sell salt in exchange of equivalent salt, sell barley in exchange of equivalent barley, but if a person transacts in excess it will be usury (Riba). This hadith enumerated 6 different commodities: gold, silver, dates, wheat, salt and barley.
- Riba Annasiah / Al Yadu (Postponement Riba): this riba takes place when two ribawi substances are exchanged, one immediately and the other with a delay. An example: two parties agree to exchange 10 kolis of gold for 2 kilos of silver such that the former is handed over immediately and the latter to be delivered 2 weeks from the date the contract is signed. Another example: two traders exchange 1 metric tons of wheat for 2 metric tons of barley such that the latter is delivered after one year.
Lending & Borrowing
- Riba Al Qardhu: constitutes any excess amount paid for extension of loans maturity date.
- Riba Al Jahilliyah : The riba prevalent in Arabia in pre - Islamic day
Buy & Sell:
- Riba Al - Fahdlu (Riba Al Hadees): actually means that excess which is taken in exchange of specific homogenous comodities and encountered in their hand to hand purchace and sale as explained in famous hadith: The Prophet said, sale gold in exchange of equivalent gold, sell silver in exchange of equivalent silver, sell dates in exchange of equivalent dates, sell wheat in exchange of equivalent wheat, sell salt in exchange of equivalent salt, sell barley in exchange of equivalent barley, but if a person transacts in excess it will be usury (Riba). This hadith enumerated 6 different commodities: gold, silver, dates, wheat, salt and barley.
- Riba Annasiah / Al Yadu (Postponement Riba): this riba takes place when two ribawi substances are exchanged, one immediately and the other with a delay. An example: two parties agree to exchange 10 kolis of gold for 2 kilos of silver such that the former is handed over immediately and the latter to be delivered 2 weeks from the date the contract is signed. Another example: two traders exchange 1 metric tons of wheat for 2 metric tons of barley such that the latter is delivered after one year.
 |
| Islamic Finance, An alternative solution to financial crisis |
- Riba Al Qardhu: constitutes any excess amount paid for extension of loans maturity date.
- Riba Al Jahilliyah : The riba prevalent in Arabia in pre - Islamic day
CONCEPT OF ISLAMIC BANKING
Contracts in Islamic Banking
The business activity can be performed through various types of contract. Some examples are:
Islamic Banking Operations
Banks are generally in the business of taking deposits and providing financing / loan. Similarly Islamic Bank aims at providing the same services to its customers. However, under tha Shariah principles, the conventional practices of lending with the repayment of interest as well as receiving deposits with payment of interest is prohibited. Thus, the practices of Islamic banks are structured slightly different at the same time maintaining its functions and core businesses of taking deposits and provide financing.
The diagram briefly explains how Islamic banking operates. In each of the process, specific Shariah contracts will be utilized to complete the process. For example, the depositor deposits money to the bank. The bank and depositor enter into Wadiah contract where the bank acts as save guardian of the money deposited.
INTRODUCTION TO ASSETS AND LIABILITES IN ISLAMIC BANKING
Assets and Liabilities in Islamic Banking
Assets
An Assets is a resource with economic value that an individual, corporation or country own or controls with the expectation that it will provide future benefit (Investopedia). Basically assets can be any belonging of value either by individuals or corporation which can be benefecial and carries value in the future use.
Liabilities
A Liability is a companys and individual financial debt or obligation that arise during a course of its business operations / life. Liabilities are settled over time through transfer of economic benefits including money, goods and services.
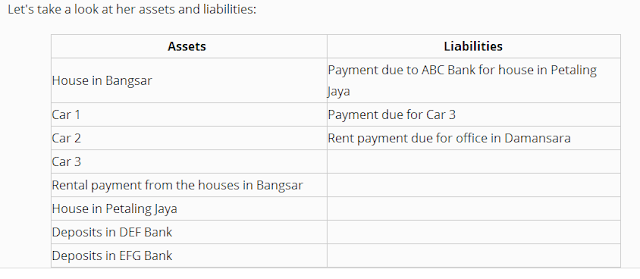
Example:
Evaluating Assets and Liabilities of Khadijah
Some of the assets are easily convertible to cash, this is what we call liquid assets, while some of the assets are long terms assets (house). However, some of the liabilities are long term like car loan while some are short term liabilities like office rental.
Assets and Liabilities in Bank
Bank have a unique balance sheets because of its nature of business.
Deposit = Liabilities
Deposits from the depositors are considered liabilities to the bank since the bank is obligated to ensured the deposits are available to depositors when they want to withdraw or when the deposit is due to be paid interest/profit (fixed-deposits) in short term period which may be different depending on different maturity.
Furthermore, this is short term liabilities since depositors has the right to withdraw the money at any time they require (saving deposits) or when the maturity is due (fixed deposit). This is also the source of funds from banks in providing financing / loan.
Financing Loans = Assets
The assets side of the bank on the other hand, is the financing or loan lent out to the customers. These financing consist of long term financing such as car loans / financing and housing loans / financing. This financing pays fixed periodic payment over a long term time span.
The table below summarizes assets and liabilities in a bank:
Banks, regardless conventional or Islamic bank are dealing with long term fixed payment assets (what they own) with short term variables liabilities (what they owes). Thus, prudent asset and liabilities management need to be in place to ensure banks meet its short term liabilities yet at the same time able to runs its business of giving financing. This is where deposits mobilisation and financing activities management plays an important role in banks.
Deposit Mobilisation in Islamic Banking
Deposit mobilisation in Islamic Banking refers to how banks collect deposits as a source of fund where this fund will be used for financing purpose on the liability side.
The most common banking system applied is:
Fractional reserve banking - Fractional reserve banking refers to a banking system in which only a fraction or proportion of the total bank deposit is utilised to be lended while a small proportion is reserved as deposit normally into the central bank. The fractional reserve is a technique that most bank use to manage their liquidity by maintaining cash reserve.
Liquidity reserved requirement - Another liquidity requirement normally enforced by the central bank is through the liquidity reserved requirement which refer to the amount that the bank require to maintain the form of cash, or gold or govt.approved securities before providing credits to the customers.
How does this system works?
Statutory reserve in Malaysia for Islamic bank is based on the Wadiah Yad Dhamanah / guaranted custody contract. It is the statutory requirement maintained with the central bank in relation to all types of customer deposits.
Liquidity requirements for Islamic bank is based on the Qard Al Hasan / benevolent loan concept. The liquidity ratio is a statutory requirement and is stipulated by the central bank from time to time.
After meeting the statutory reserve requirements and holding the required level of liquid assets, Islamic banks, generally, provide the funds using three major categories of financing modes: sale, leasing and sharing, where sale and leasing modes are debt based while sharing is equity based.
Profit Distribution Methodology between Depositor and The Bank
Any funds from pool of deposit will be deducted for Statutory Reserve Requirement and Liquidity Reserve Requirements.
The balance will be used as funding sources for financing activities. Surplus of fund after financing activities will be invested in Islamic Inter - Bank Money Market (IIMM), while when in the shortage position, fund will be sourcing from IIMM to cover their shortage.
The financing / investment activities will generate fix periodical profit which is then pooled before distributed to the depositors and investors.
The financing activities will be one of one main components of banking business where it utilises the deposits collected to finance customers consumption. Normally, bank will charge interest / profit rate higher than the deposit profit rate so as to manage their operaion cost as well as to generate profit.
Financing Activities in Islamic Banking
Financing activities in banks is the largest business component in banking activities.
The financing activities form the long term assets of the bank in the sense that it generates long term fixed income from the financing that were given out.
The income generated from these activities are then collected and pooled. After making the necessary deduction and provision, the income will be distributed accordingly to the depositors.
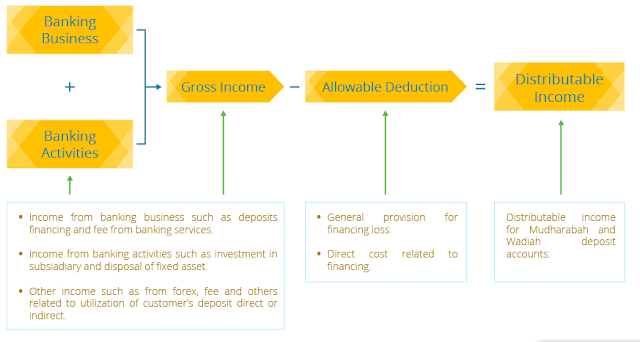
Deriving Distributable Income in Banking Operations
The process of deriving the distributable income for the depositors and investors is through pooling the income generated from both the banking business and banking activities after taking into consideration the allowable deduction or provision. The diagram below will explain briefly the processof deriving the distributable income.
Brief Introduction to Islamic Bank Financing Activities
The financing activities in a bank can be classified into consumer / retail financing and corporate banking. Retail financing refers to financing given out to retails customers.
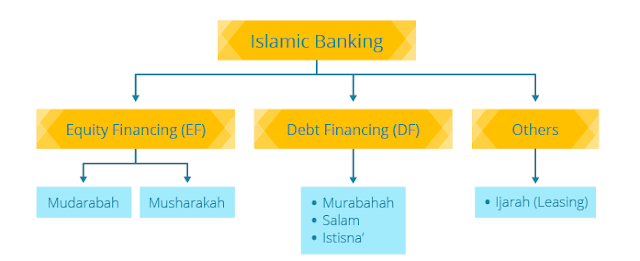
How do Islamic banks givie this financing?
The basis for Islamic banking products is derived by applying some of the Shariah compliant contract. Islamic bank financing activities may provide financing in form of equity financing through partnership contracts of Mushakarah (profit and loss sharing capital) and Mudharabah (profit sharing capital). In addition to that, the Islamic banks also provide the various types of debt financing through contract such as Murabahah, Salam, Istisna.
Islamic Banks in two Islamic Countries: United Arab Emirates and Brunei Darussalam
- Central Bank of United Arab Emirates (UAE) - There is a Federal Law No.6 of 1985 Regarding Islamic Banks, Financial Institutions and Investment companies. In Brunei Darussalam, There is an Autoriti Monetari Brunei Darussalam (AMBD). Islamic Banking was first introduced in Brunei Darussalam in 1990. In 2010, Islamic Finance held held a significant role in Banking Industry with total assets of B$6.36 billion and deposits totalling B$5.167 billion which accounted for 37% and 34.6% of the total market share. In Brunei Darussalam, Islamic Banking and Finance has become one of the primary sectors of focus in the financial services indutry. At present, the Islamic financial services cover banking, takaful, asset management, mutual funds and trust services.
- Both countries United Arab Emirates and Brunei Darussalam, have established the Syariah Governance and Supervision Boards with the duty of ascertaining that all Islamic products are in accordance with Syariah law before they are allowed to be distributed. In UAE, the Shariah Supervision and Authority shall be formed of minimum three members to render their transactions and practices accordant with the principles and and provisions of Islamic Shariah Law.
Read More:
https://www.openlearning.com/inceif/courses/intro-to-islamic-banking/what_is_banking_system




































No comments:
Post a Comment